There are different approaches to mounting components onto a printed circuit board with each method having its own strengths and weaknesses. This brings up the need of understanding what a given circuit is expected to do hence going for an approach that will bring the best in terms or performance and durability out your circuit.
Surface Mounted Technology (SMT) is one such approach that works by mounting the circuit components directly onto the printed circuit board resulting into what is called a surface mount device. This is a common replacement for the traditional soldering into holes in a circuit board since it results to tightly squeezed and versatile builds.
mount device. This is a common replacement for the traditional soldering into holes in a circuit board since it results to tightly squeezed and versatile builds.
There are some important things to know before venturing into SMT;
-
SMT Production does not work in all cases
It is important to know that SMT does not support all types of applications in a circuit. While the technology is right with most of the tasks that traditional soldering can address, it cannot handle some special cases. For instance, the soldering of transformers and mounting of heat sinks must be done the traditional way if at all these components has to work properly.
-
The procedure to doing the job
A specially designed printed circuit board is needed for the job. In automated placement, components to be added to the circuit board are placed onto the PCB by pick-and-place machines before the board is placed in a reflow soldering oven, which slowly and uniformly raises the board’s temperature until the thin film of solder material melts and clamps the components into place. The function of the reflow oven varies depending on the design concerns with the most common being infrared lamps, hot gas convection and use of special fluorocarbon liquids.
-
Tools needed for the job
To achieve the desired environment in SMT production, you have to use the right tools that depend on the precision of the job you do. The choice of tools, board material and ovens, you have to determine the design of your circuit before making the call. The tools used in an SMT procedure dictate the success or failure of product.
-
Advantages
The bright side of SMT assembly lies in the fact that these techniques can handler smaller components and achieve higher component density. With the option to solder onto both sides of the board and lower induction and induction at the contacts, this technique is the solution to creation of highly integrated circuits that are on high demand, as miniaturization of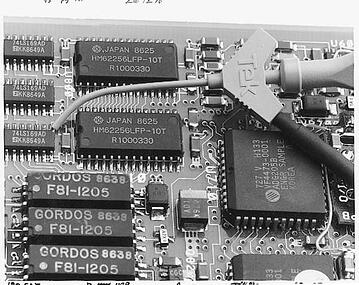 components becomes the order of the day.
components becomes the order of the day.
-
Disadvantages
On the other hand, problems come with the SMT manufacturing. For instance, the techniques makes repair difficult in case the equipment needs to have some components replaced, SMT components do not work with plug in breadboards, is unsuitable for high power components like electric circuits and is not a good way of creating contacts for connectors that interface with outer world hence subject to frequent mechanical stress.
Analyze your market and learn the legislations governing the market
Before venturing into SMT manufacturing, you have to be sure that you have the demand. SMT equipment has very high capacity and requires trained personnel and engineers. You have to weigh the market to ensure that you do not invest in hardware that will lie to waste in a ware house waiting for meager contracts in on and off basis.
Finally, you must understand that there are some conventions set up by different quality management firms to ensure that equipment delivered to the market are up to standard. To remain on the safe side of the law and other regulations, ensure that your operations remain legal and top quality to maintain your reputation in the market