When new clients come to us asking for assistance in bringing a product to market, it's often because they've become overwhelmed by the sheer number of options when it comes to PCB assembly and manufacturing.
When new clients come to us asking for assistance in bringing a product to market, it's often because they've become overwhelmed by the sheer number of options when it comes to PCB assembly and manufacturing.
Rapid technological changes have created an environment where even seemingly-minor issues like those of electronic interconnect cables are far more important than they seem.
Electronic interconnect cables are exactly what they sound like. The wiring on the underside of a PCB is designed to carry current, not data. So on a modern PCB with multiple processing units and other "smart" components, they need additional wiring to carry the data between those components. Additionally, they're needed to carry data to/from any external sensors, displays, or other components the user may interact with.
They're actually a very key issue to creating a circuit board, and a final product, that lives up to the initial design specs.
Major Factors That Influence The Success Of Electronic Interconnections
1 - Wire Materials
As with standard electronics, your major choices in wiring boil down to copper vs fiber, with copper being the more cost-efficient option. However, copper is often not the savings one might expect. The high speeds of fiber optic cabling mean that you often need several copper wires in place of one fiber line, negating most or all of the cost savings.
Good design labs have simulators in place that can determine optimal wiring materials, in terms of lines vs cost.
2 - Stackup Planes
Very often, a single layer of interconnect wiring isn't enough to support the data needs of a circuit board. However, due to interference, they can't be layered directly onto each other. There has to be a separate layer of grounding planes to keep the signals from interfering. In modern PCBs, there can sometimes be up to fifty of these alternating stacks, all sandwiched onto the back of the board.
High-precision equipment is necessary to layer those elements correctly, so that they don't interfere with each other.
3 - Insulating materials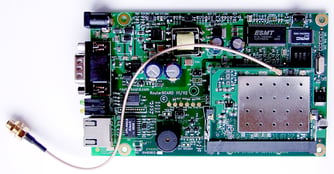
The insulation around electronic interconnect cables -also called dilectrics- can make a big difference. This is a case where cost and performance are almost exactly aligned. Older, cheaper materials such as fiberglass-epoxy FR-4 provide adequate insulation, but can have heat and interference limitations. Newer materials like Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) or Teflon provide better heat protection, and more signal containment.
A good PCB assembly partner will talk you through the choice here, and may have options for mix-and-matching materials to create a best-of-both-worlds solution.
4 - Latency
Latency is simply "how long does it take data to travel from A to B." Lower latencies are almost always better, within the confines of existing processor/memory capabilities. Latency is affected by all of the above, and more, and is one of the key things a good PCB prototyping and assembly service looks to optimize.
This is also a great example of where full-service electronics services can help you lower your costs. Latency is affected by physical distance as well, so a manufacturer with good simulation services can find optimal combinations of layout, materials, and wiring to bring the lowest latencies at the lowest costs.
Are you looking to bring a new electronics product to market? Contact the experts at ZenTech today for a full consultation on our many value-added service offerings.