Counterfeit electronic components is an age-old issue, but is growing in exponential proportions with respect to the types of products being counterfeited, industries being affected and potential consequences caused by counterfeits.
If this threat is not adequately addressed, counterfeit items have the potential to seriously compromise the safety and operational effectiveness of customer’s products.
What is Counterfeit Electronic Components?
SAE AS5553 Standard for "Fraudulent/Counterfeit Electronic Parts; Avoidance, Detection, Mitigation, and Disposition" defines counterfeit part as "a fraudulent part that has been confirmed to be a copy, imitation, or substitute that has been represented, identified, or marked as genuine, and / or altered by a source without legal right with intent to mislead, deceive, or defraud”.
According to the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), a Counterfeit Part is a part made or altered so as to imitate or resemble an “approved part” without authority or right, and with the intent to mislead or defraud by passing the imitation as original or genuine.*
Causes
Design and Logistics
- Parts obsolescence
- Insufficient inventory for product design life
Procurement
- Failure to procure from trusted/authorized sources (cost/schedule driven)
- Failure to procure data deliverables for traceability and authentication
- Failure to invoke rigid quality assurance requirements
Manufacturers
- Dumping of excess inventory without traceability
- Excessive lead times
Independent Non-Franchised Distributors (Brokers)
- Inadequate or nonexistent Quality Assurance
- Deliberate misrepresentation of product
Governmental Regulations
- Electronic parts reclamation (e-waste) and Pb-free solder requirements
Quality Assurance
- Inadequate test and inspection practices to detect counterfeiting
Law enforcement authorities
- Insufficient resources for tracking down and prosecuting counterfeiters
Impact
- Personal injury / loss of life
- Mission failure
- Reduced reliability and product recalls
- Potential loss of contracts
- Shutdown of manufacturing lines
- Negative cost and schedule impacts
- Penalties for companies and individuals
- Damage to corporate image
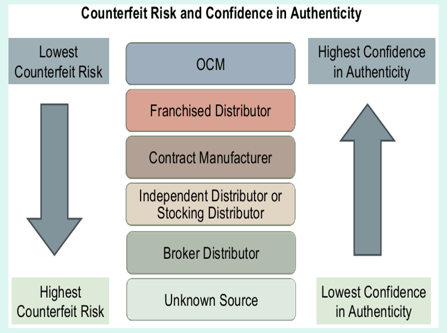 Best Practices
Best Practices
- Parts Obsolescence Management
- Anticipate obsolescence issues in time to initiate actions such as redesign or lifetime buys - Source Selection
- Require the exclusive utilization of OCMs/OEMs or their authorized distributors - Chain of Custody
- Require a documented unbroken chain of custody from the original source of manufacture for all components provided - Quality system audits and/or counterfeit parts mitigation process audits
- Equipment providers (e.g., AS9100)
- Distributors (e.g., AS9120)
- Contract Manufacturer/Assembler (if they procure parts for the customer) - Review the supplier's returns process (RMA) as applicable
- A weak returns process is one way an otherwise good supplier (authorized or not) could be exposed and inadvertently pass on counterfeit components. - Parts authentication tools
- In-house counterfeit awareness and detection training
*source: Detecting and Reporting Suspected Unapproved Parts, 03/13/00 FAA advisory Circular No. 21-29B
About Zentech: Zentech Manufacturing, Inc. is a privately held, engineering-driven contract manufacturer specializing in the design and manufacture of highly-complex electronic and RF circuit cards and assemblies. The company is headquartered in its purpose-built facility located in Baltimore, MD and maintains several
key certifications, including ISO 9001:2008, ITAR (US State Dept.), AS9100 (aerospace), and ISO 13485 (medical). In addition, Zentech is a certified IPC Trusted Source supplier for Class 3 mission-critical electronics, and the company is IPC J-STD-001 Space Addendum QML certified.